PyQt FAQ Layout Management
–Ь–∞—В–µ—А–Є–∞–ї –Є–Ј Wiki.crossplatform.ru
(–Э–Њ–≤–∞—П: Important thing in programming is the layout management. Layout management is the way how we place the widgets on the window. The management can be done in two ways. We can use <b>absolu...)
–°–ї–µ–і—Г—О—Й–∞—П –њ—А–∞–≤–Ї–∞ вЖТ
–Т–µ—А—Б–Є—П 11:11, 18 —Д–µ–≤—А–∞–ї—П 2009
Important thing in programming is the layout management. Layout management is the way how we place the widgets on the window. The management can be done in two ways. We can use absolute positioning or layout classes.
Absolute positioning
The programmer specifies the position and the size of each widget in pixels. When you use absolute positioning, you have to understand several things.
- the size and the position of a widget do not change, if you resize a window
- applications might look different on various platforms
- changing fonts in your application might spoil the layout
- if you decide to change your layout, you must completely redo your layout, which is tedious and time consuming
#!/usr/bin/python # absolute.py import sys from PyQt4 import QtGui class Absolute(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self, parent=None): QtGui.QWidget.__init__(self, parent) self.setWindowTitle('Communication') label = QtGui.QLabel('Couldn\'t', self) label.move(15, 10) label = QtGui.QLabel('care', self) label.move(35, 40) label = QtGui.QLabel('less', self) label.move(55, 65) label = QtGui.QLabel('And', self) label.move(115, 65) label = QtGui.QLabel('then', self) label.move(135, 45) label = QtGui.QLabel('you', self) label.move(115, 25) label = QtGui.QLabel('kissed', self) label.move(145, 10) label = QtGui.QLabel('me', self) label.move(215, 10) self.resize(250, 150) app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv) qb = Absolute() qb.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())
We simply call the move() method to position our widgets. In our case QLabel-s. We position them by providing the x and the y coordinates. The beginning of the coordinate system is at the left top corner. The x values grow from left to right. The y values grow from top to bottom.
Box Layout
Layout management with layout classes is much more flexible and practical. It is the preferred way to place widgets on a window. The basic layout classes are QHBoxLayout and QVBoxLayout. They line up widgets horizontally and vertically.
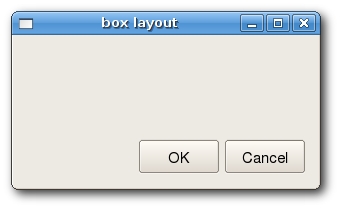
Imagine that we wanted to place two buttons in the right bottom corner. To create such a layout, we will use one horizontal and one vertical box. To create the neccessary space, we will add a stretch factor.
#!/usr/bin/python # boxlayout.py import sys from PyQt4 import QtGui class BoxLayout(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self, parent=None): QtGui.QWidget.__init__(self, parent) self.setWindowTitle('box layout') ok = QtGui.QPushButton("OK") cancel = QtGui.QPushButton("Cancel") hbox = QtGui.QHBoxLayout() hbox.addStretch(1) hbox.addWidget(ok) hbox.addWidget(cancel) vbox = QtGui.QVBoxLayout() vbox.addStretch(1) vbox.addLayout(hbox) self.setLayout(vbox) self.resize(300, 150) app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv) qb = BoxLayout() qb.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())
ok = QtGui.QPushButton("OK") cancel = QtGui.QPushButton("Cancel")
Here we create two push buttons.
hbox = QtGui.QHBoxLayout() hbox.addStretch(1) hbox.addWidget(ok) hbox.addWidget(cancel)
We create a horizontal box layout. Add a stretch factor and both buttons.
vbox = QtGui.QVBoxLayout() vbox.addStretch(1) vbox.addLayout(hbox)
To create the necessary layout, we put a horizontal lauout into a vertical one.
self.setLayout(vbox)
Finally, we set the main layout of the window.
QGridLayout
The most universal layout class is the grid layout. This layout divides the space into rows and columns. To create a grid layout, we use the QGridLayout class.
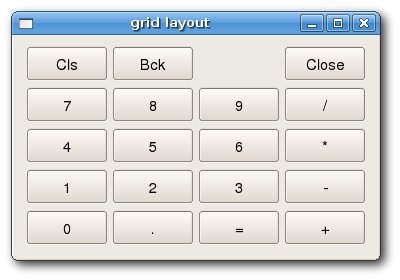
#!/usr/bin/python # gridlayout.py import sys from PyQt4 import QtGui class GridLayout(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self, parent=None): QtGui.QWidget.__init__(self, parent) self.setWindowTitle('grid layout') names = ['Cls', 'Bck', '', 'Close', '7', '8', '9', '/', '4', '5', '6', '*', '1', '2', '3', '-', '0', '.', '=', '+'] grid = QtGui.QGridLayout() j = 0 pos = [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (0, 3), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 0), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 0), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3 ), (4, 0), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3)] for i in names: button = QtGui.QPushButton(i) if j == 2: grid.addWidget(QtGui.QLabel(''), 0, 2) else: grid.addWidget(button, pos[j][0], pos[j][1]) j = j + 1 self.setLayout(grid) app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv) qb = GridLayout() qb.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())
In our example, we create a grid of buttons. To fill one gap, we add one QLabel widget.
grid = QtGui.QGridLayout()
Here we create a grid layout.
if j == 2: grid.addWidget(QtGui.QLabel(''), 0, 2) else: grid.addWidget(button, pos[j][0], pos[j][1])
To add a widget to a grid, we call the addWidget() method. The arguments are the widget, the row and the column number.
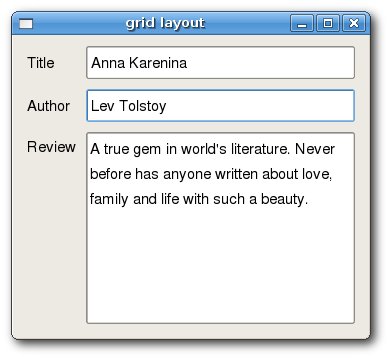
Widgets can span multiple columns or rows in a grid. In the next example we illustrate this.
#!/usr/bin/python # gridlayout2.py import sys from PyQt4 import QtGui class GridLayout2(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self, parent=None): QtGui.QWidget.__init__(self, parent) self.setWindowTitle('grid layout') title = QtGui.QLabel('Title') author = QtGui.QLabel('Author') review = QtGui.QLabel('Review') titleEdit = QtGui.QLineEdit() authorEdit = QtGui.QLineEdit() reviewEdit = QtGui.QTextEdit() grid = QtGui.QGridLayout() grid.setSpacing(10) grid.addWidget(title, 1, 0) grid.addWidget(titleEdit, 1, 1) grid.addWidget(author, 2, 0) grid.addWidget(authorEdit, 2, 1) grid.addWidget(review, 3, 0) grid.addWidget(reviewEdit, 3, 1, 5, 1) self.setLayout(grid) self.resize(350, 300) app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv) qb = GridLayout2() qb.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())
grid = QtGui.QGridLayout() grid.setSpacing(10)
We create a grid layout and set spacing between widgets.
grid.addWidget(reviewEdit, 3, 1, 5, 1)
If we add a widget to a grid, we can provide row span and column span of the widget. In our case, we make the reviewEdit widget span 5 rows.