PyGTK FAQ Dialogs
РңР°СӮРөСҖиал РёР· Wiki.crossplatform.ru
(вҶ’Message dialogs) |
(РёСҒРҝСҖавил РҪазваРҪРёРө РәР°СӮРөРіРҫСҖРёРё) |
||
| РЎСӮСҖРҫРәР° 341: | РЎСӮСҖРҫРәР° 341: | ||
[[РҡР°СӮРөРіРҫСҖРёСҸ:Python]] | [[РҡР°СӮРөРіРҫСҖРёСҸ:Python]] | ||
| - | [[РҡР°СӮРөРіРҫСҖРёСҸ:GTK]] | + | [[РҡР°СӮРөРіРҫСҖРёСҸ:GTK+]] |
Р’РөСҖСҒРёСҸ 16:41, 19 С„РөРІСҖалСҸ 2009
In this part of the PyGTK programming tutorial, we will introduce dialogs.
Dialog windows or dialogs are an indispensable part of most modern GUI applications. A dialog is defined as a conversation between two or more persons. In a computer application a dialog is a window which is used to "talk" to the application. And vice versa. A dialog is used to input data, modify data, change the application settings etc. Dialogs are important means of communication between a user and a computer program.
РЎРҫРҙРөСҖжаРҪРёРө |
Message dialogs
Message dialogs are convenient dialogs that provide messages to the user of the application. The message consists of textual and image data.
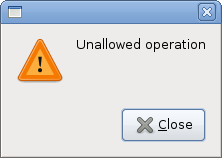
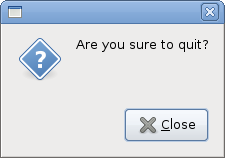
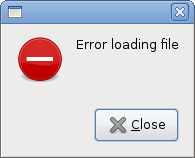
#!/usr/bin/python # ZetCode PyGTK tutorial # # This example shows message # dialogs # # author: jan bodnar # website: zetcode.com # last edited: February 2009 import gtk class PyApp(gtk.Window): def __init__(self): super(PyApp, self).__init__() self.set_size_request(250, 100) self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER) self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit) self.set_title("Message dialogs") table = gtk.Table(2, 2, True); info = gtk.Button("Information") warn = gtk.Button("Warning") ques = gtk.Button("Question") erro = gtk.Button("Error") info.connect("clicked", self.on_info) warn.connect("clicked", self.on_warn) ques.connect("clicked", self.on_ques) erro.connect("clicked", self.on_erro) table.attach(info, 0, 1, 0, 1) table.attach(warn, 1, 2, 0, 1) table.attach(ques, 0, 1, 1, 2) table.attach(erro, 1, 2, 1, 2) self.add(table) self.show_all() def on_info(self, widget): md = gtk.MessageDialog(self, gtk.DIALOG_DESTROY_WITH_PARENT, gtk.MESSAGE_INFO, gtk.BUTTONS_CLOSE, "Download completed") md.run() md.destroy() def on_erro(self, widget): md = gtk.MessageDialog(self, gtk.DIALOG_DESTROY_WITH_PARENT, gtk.MESSAGE_ERROR, gtk.BUTTONS_CLOSE, "Error loading file") md.run() md.destroy() def on_ques(self, widget): md = gtk.MessageDialog(self, gtk.DIALOG_DESTROY_WITH_PARENT, gtk.MESSAGE_QUESTION, gtk.BUTTONS_CLOSE, "Are you sure to quit?") md.run() md.destroy() def on_warn(self, widget): md = gtk.MessageDialog(self, gtk.DIALOG_DESTROY_WITH_PARENT, gtk.MESSAGE_WARNING, gtk.BUTTONS_CLOSE, "Unallowed operation") md.run() md.destroy() PyApp() gtk.main()
In our example, we will show four kinds of message dialogs. Information, Warning, Question and Error message dialogs.
info = gtk.Button("Information") warn = gtk.Button("Warning") ques = gtk.Button("Question") erro = gtk.Button("Error")
We have four buttons. Each of these buttons will show a different kind of message dialog.
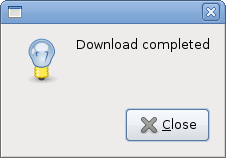
md = gtk.MessageDialog(self, gtk.DIALOG_DESTROY_WITH_PARENT, gtk.MESSAGE_INFO, gtk.BUTTONS_CLOSE, "Download completed") md.run() md.destroy()
If we click on the info button, the Information dialog is displayed. The MESSAGE_INFO specifies the type of the dialog. The BUTTONS_CLOSE specifies the button to be displayed in the dialog. The last parameter is the message dislayed. The dialog is displayed with the run() method. The programmer must also call either the destroy() or the hide() method.
| 
|
| 
|
AboutDialog
The AboutDialog displays information about the application.
AboutDialog can display a logo, the name of the application, version, copyright, website or licence information. It is also possible to give credits to the authors, documenters, translators and artists.
#!/usr/bin/python # ZetCode PyGTK tutorial # # This example demonstrates the # AboutDialog dialog # # author: jan bodnar # website: zetcode.com # last edited: February 2009 import gtk class PyApp(gtk.Window): def __init__(self): super(PyApp, self).__init__() self.set_size_request(300, 150) self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER) self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit) self.set_title("About battery") button = gtk.Button("About") button.set_size_request(80, 30) button.connect("clicked", self.on_clicked) fix = gtk.Fixed() fix.put(button, 20, 20) self.add(fix) self.show_all() def on_clicked(self, widget): about = gtk.AboutDialog() about.set_program_name("Battery") about.set_version("0.1") about.set_copyright("(c) Jan Bodnar") about.set_comments("Battery is a simple tool for battery checking") about.set_website("http://www.zetcode.com") about.set_logo(gtk.gdk.pixbuf_new_from_file("battery.png")) about.run() about.destroy() PyApp() gtk.main()
The code example uses a AboutDialog with some of it's features.
about = gtk.AboutDialog()
We create an AboutDialog.
about = gtk.AboutDialog() about.set_program_name("Battery") about.set_version("0.1") about.set_copyright("(c) Jan Bodnar")
We specify the name, version and the copyright.
about.set_logo(gtk.gdk.pixbuf_new_from_file("battery.png"))
This line creates a logo.
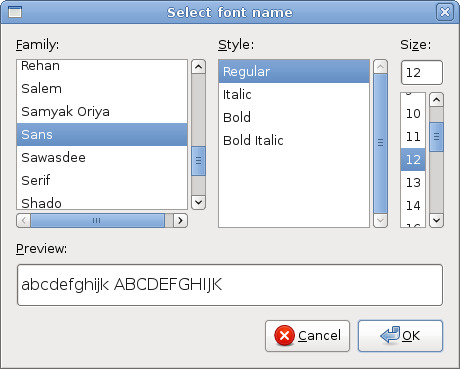
FontSelectionDialog
The FontSelectionDialog is a dialog for selecting fonts. It is typically used in applications, that do some text editing or formatting.
#!/usr/bin/python # ZetCode PyGTK tutorial # # This example works with the # FontSelection dialog # # author: jan bodnar # website: zetcode.com # last edited: February 2009 import gtk import pango class PyApp(gtk.Window): def __init__(self): gtk.Window.__init__(self) self.set_size_request(300, 150) self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER) self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit) self.set_title("Font Selection Dialog") self.label = gtk.Label("The only victory over love is flight.") button = gtk.Button("Select font") button.connect("clicked", self.on_clicked) fix = gtk.Fixed() fix.put(button, 100, 30) fix.put(self.label, 30, 90) self.add(fix) self.show_all() def on_clicked(self, widget): fdia = gtk.FontSelectionDialog("Select font name") response = fdia.run() if response == gtk.RESPONSE_OK: font_desc = pango.FontDescription(fdia.get_font_name()) if font_desc: self.label.modify_font(font_desc) fdia.destroy() PyApp() gtk.main()
In the code example, we have a button and a label. We show the FontSelectionDialog by clicking on the button.
fdia = gtk.FontSelectionDialog("Select font name")
We create the FontSelectionDialog.
if response == gtk.RESPONSE_OK: font_desc = pango.FontDescription(fdia.get_font_name()) if font_desc: self.label.modify_font(font_desc)
If we click on the OK button, the font of the label widget changes to the one, that we selected in the dialog.
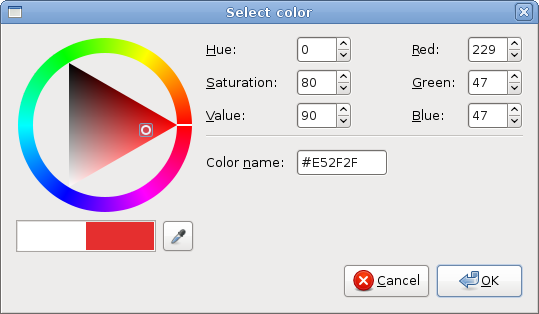
ColorSelectionDialog
ColorSelectionDialog is a dialog for selecting a color.
#!/usr/bin/python # ZetCode PyGTK tutorial # # This example works with the # ColorSelection dialog # # author: jan bodnar # website: zetcode.com # last edited: February 2009 import gtk class PyApp(gtk.Window): def __init__(self): super(PyApp, self).__init__() self.set_size_request(300, 150) self.set_position(gtk.WIN_POS_CENTER) self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit) self.set_title("Color Selection Dialog") self.label = gtk.Label("The only victory over love is flight.") button = gtk.Button("Select color") button.connect("clicked", self.on_clicked) fix = gtk.Fixed() fix.put(button, 100, 30) fix.put(self.label, 30, 90) self.add(fix) self.show_all() def on_clicked(self, widget): cdia = gtk.ColorSelectionDialog("Select color") response = cdia.run() if response == gtk.RESPONSE_OK: colorsel = cdia.colorsel color = colorsel.get_current_color() self.label.modify_fg(gtk.STATE_NORMAL, color) cdia.destroy() PyApp() gtk.main()
The example is very similar to the previous one. This time we change the color of the label.
cdia = gtk.ColorSelectionDialog("Select color")
We create the ColorSelectionDialog.
if response == gtk.RESPONSE_OK: colorsel = cdia.colorsel color = colorsel.get_current_color() self.label.modify_fg(gtk.STATE_NORMAL, color)
If the user pressed OK, we get the color and modify the label's color.
In this part of the PyGTK programming tutorial, we worked with PyGTK built-in dialogs.