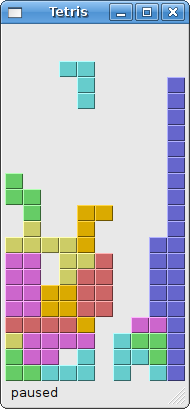
PyQt FAQ The Tetris game
РңР°СӮРөСҖиал РёР· Wiki.crossplatform.ru
(РқРҫРІР°СҸ: Creating a computer game is very challenging. Sooner or later, a programmer will want to create a computer game one day. In fact, many people became interested in programming, because th...)
РЎР»РөРҙСғСҺСүР°СҸ РҝСҖавРәР° вҶ’
Р’РөСҖСҒРёСҸ 11:23, 18 С„РөРІСҖалСҸ 2009
Creating a computer game is very challenging. Sooner or later, a programmer will want to create a computer game one day. In fact, many people became interested in programming, because they played games and wanted to create their own. Creating a computer game will vastly help improving your programming skills.
Tetris
The tetris game is one of the most popular computer games ever created. The original game was designed and programmed by a russian programmer Alexey Pajitnov in 1985. Since then, tetris is available on almost every computer platform in lots of variations. Even my mobile phone has a modified version of the tetris game.
Tetris is called a falling block puzzle game. In this game, we have seven different shapes called tetrominoes. S-shape, Z-shape, T-shape, L-shape, Line-shape, MirroredL-shape and a Square-shape. Each of these shapes is formed with four squares. The shapes are falling down the board. The object of the tetris game is to move and rotate the shapes, so that they fit as much as possible. If we manage to form a row, the row is destroyed and we score. We play the tetris game until we top out.
PyQt4 is a toolkit designed to create applications. There are other libraries which are targeted at creating computer games. Nevertheless, PyQt4 and other application toolkits can be used to create games.
The following example is a modified version of the tetris game, available with PyQt4 installation files.
The development
We do not have images for our tetris game, we draw the tetrominoes using the drawing API available in the PyQt4 programming toolkit. Behind every computer game, there is a mathematical model. So it is in tetris.
Some ideas behind the game.
- We use QtCore.QBasicTimer() to create a game cycle
- The tetrominoes are drawn
- The shapes move on a square by square basis (not pixel by pixel)
- Mathematically a board is a simple list of numbers
#!/usr/bin/python # tetris.py import sys import random from PyQt4 import QtCore, QtGui class Tetris(QtGui.QMainWindow): def __init__(self): QtGui.QMainWindow.__init__(self) self.setGeometry(300, 300, 180, 380) self.setWindowTitle('Tetris') self.tetrisboard = Board(self) self.setCentralWidget(self.tetrisboard) self.statusbar = self.statusBar() self.connect(self.tetrisboard, QtCore.SIGNAL("messageToStatusbar(QString)"), self.statusbar, QtCore.SLOT("showMessage(QString)")) self.tetrisboard.start() self.center() def center(self): screen = QtGui.QDesktopWidget().screenGeometry() size = self.geometry() self.move((screen.width()-size.width())/2, (screen.height()-size.height())/2) class Board(QtGui.QFrame): BoardWidth = 10 BoardHeight = 22 Speed = 300 def __init__(self, parent): QtGui.QFrame.__init__(self, parent) self.timer = QtCore.QBasicTimer() self.isWaitingAfterLine = False self.curPiece = Shape() self.nextPiece = Shape() self.curX = 0 self.curY = 0 self.numLinesRemoved = 0 self.board = [] self.setFocusPolicy(QtCore.Qt.StrongFocus) self.isStarted = False self.isPaused = False self.clearBoard() self.nextPiece.setRandomShape() def shapeAt(self, x, y): return self.board[(y * Board.BoardWidth) + x] def setShapeAt(self, x, y, shape): self.board[(y * Board.BoardWidth) + x] = shape def squareWidth(self): return self.contentsRect().width() / Board.BoardWidth def squareHeight(self): return self.contentsRect().height() / Board.BoardHeight def start(self): if self.isPaused: return self.isStarted = True self.isWaitingAfterLine = False self.numLinesRemoved = 0 self.clearBoard() self.emit(QtCore.SIGNAL("messageToStatusbar(QString)"), str(self.numLinesRemoved)) self.newPiece() self.timer.start(Board.Speed, self) def pause(self): if not self.isStarted: return self.isPaused = not self.isPaused if self.isPaused: self.timer.stop() self.emit(QtCore.SIGNAL("messageToStatusbar(QString)"), "paused") else: self.timer.start(Board.Speed, self) self.emit(QtCore.SIGNAL("messageToStatusbar(QString)"), str(self.numLinesRemoved)) self.update() def paintEvent(self, event): painter = QtGui.QPainter(self) rect = self.contentsRect() boardTop = rect.bottom() - Board.BoardHeight * self.squareHeight() for i in range(Board.BoardHeight): for j in range(Board.BoardWidth): shape = self.shapeAt(j, Board.BoardHeight - i - 1) if shape != Tetrominoes.NoShape: self.drawSquare(painter, rect.left() + j * self.squareWidth(), boardTop + i * self.squareHeight(), shape) if self.curPiece.shape() != Tetrominoes.NoShape: for i in range(4): x = self.curX + self.curPiece.x(i) y = self.curY - self.curPiece.y(i) self.drawSquare(painter, rect.left() + x * self.squareWidth(), boardTop + (Board.BoardHeight - y - 1) * self.squareHeight(), self.curPiece.shape()) def keyPressEvent(self, event): if not self.isStarted or self.curPiece.shape() == Tetrominoes.NoShape: QtGui.QWidget.keyPressEvent(self, event) return key = event.key() if key == QtCore.Qt.Key_P: self.pause() return if self.isPaused: return elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Left: self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX - 1, self.curY) elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Right: self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX + 1, self.curY) elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Down: self.tryMove(self.curPiece.rotatedRight(), self.curX, self.curY) elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Up: self.tryMove(self.curPiece.rotatedLeft(), self.curX, self.curY) elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Space: self.dropDown() elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_D: self.oneLineDown() else: QtGui.QWidget.keyPressEvent(self, event) def timerEvent(self, event): if event.timerId() == self.timer.timerId(): if self.isWaitingAfterLine: self.isWaitingAfterLine = False self.newPiece() else: self.oneLineDown() else: QtGui.QFrame.timerEvent(self, event) def clearBoard(self): for i in range(Board.BoardHeight * Board.BoardWidth): self.board.append(Tetrominoes.NoShape) def dropDown(self): newY = self.curY while newY > 0: if not self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX, newY - 1): break newY -= 1 self.pieceDropped() def oneLineDown(self): if not self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX, self.curY - 1): self.pieceDropped() def pieceDropped(self): for i in range(4): x = self.curX + self.curPiece.x(i) y = self.curY - self.curPiece.y(i) self.setShapeAt(x, y, self.curPiece.shape()) self.removeFullLines() if not self.isWaitingAfterLine: self.newPiece() def removeFullLines(self): numFullLines = 0 rowsToRemove = [] for i in range(Board.BoardHeight): n = 0 for j in range(Board.BoardWidth): if not self.shapeAt(j, i) == Tetrominoes.NoShape: n = n + 1 if n == 10: rowsToRemove.append(i) rowsToRemove.reverse() for m in rowsToRemove: for k in range(m, Board.BoardHeight): for l in range(Board.BoardWidth): self.setShapeAt(l, k, self.shapeAt(l, k + 1)) numFullLines = numFullLines + len(rowsToRemove) if numFullLines > 0: self.numLinesRemoved = self.numLinesRemoved + numFullLines self.emit(QtCore.SIGNAL("messageToStatusbar(QString)"), str(self.numLinesRemoved)) self.isWaitingAfterLine = True self.curPiece.setShape(Tetrominoes.NoShape) self.update() def newPiece(self): self.curPiece = self.nextPiece self.nextPiece.setRandomShape() self.curX = Board.BoardWidth / 2 + 1 self.curY = Board.BoardHeight - 1 + self.curPiece.minY() if not self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX, self.curY): self.curPiece.setShape(Tetrominoes.NoShape) self.timer.stop() self.isStarted = False self.emit(QtCore.SIGNAL("messageToStatusbar(QString)"), "Game over") def tryMove(self, newPiece, newX, newY): for i in range(4): x = newX + newPiece.x(i) y = newY - newPiece.y(i) if x < 0 or x >= Board.BoardWidth or y < 0 or y >= Board.BoardHeight: return False if self.shapeAt(x, y) != Tetrominoes.NoShape: return False self.curPiece = newPiece self.curX = newX self.curY = newY self.update() return True def drawSquare(self, painter, x, y, shape): colorTable = [0x000000, 0xCC6666, 0x66CC66, 0x6666CC, 0xCCCC66, 0xCC66CC, 0x66CCCC, 0xDAAA00] color = QtGui.QColor(colorTable[shape]) painter.fillRect(x + 1, y + 1, self.squareWidth() - 2, self.squareHeight() - 2, color) painter.setPen(color.light()) painter.drawLine(x, y + self.squareHeight() - 1, x, y) painter.drawLine(x, y, x + self.squareWidth() - 1, y) painter.setPen(color.dark()) painter.drawLine(x + 1, y + self.squareHeight() - 1, x + self.squareWidth() - 1, y + self.squareHeight() - 1) painter.drawLine(x + self.squareWidth() - 1, y + self.squareHeight() - 1, x + self.squareWidth() - 1, y + 1) class Tetrominoes(object): NoShape = 0 ZShape = 1 SShape = 2 LineShape = 3 TShape = 4 SquareShape = 5 LShape = 6 MirroredLShape = 7 class Shape(object): coordsTable = ( ((0, 0), (0, 0), (0, 0), (0, 0)), ((0, -1), (0, 0), (-1, 0), (-1, 1)), ((0, -1), (0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1)), ((0, -1), (0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2)), ((-1, 0), (0, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1)), ((0, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 1)), ((-1, -1), (0, -1), (0, 0), (0, 1)), ((1, -1), (0, -1), (0, 0), (0, 1)) ) def __init__(self): self.coords = [[0,0] for i in range(4)] self.pieceShape = Tetrominoes.NoShape self.setShape(Tetrominoes.NoShape) def shape(self): return self.pieceShape def setShape(self, shape): table = Shape.coordsTable[shape] for i in range(4): for j in range(2): self.coords[i][j] = table[i][j] self.pieceShape = shape def setRandomShape(self): self.setShape(random.randint(1, 7)) def x(self, index): return self.coords[index][0] def y(self, index): return self.coords[index][1] def setX(self, index, x): self.coords[index][0] = x def setY(self, index, y): self.coords[index][1] = y def minX(self): m = self.coords[0][0] for i in range(4): m = min(m, self.coords[i][0]) return m def maxX(self): m = self.coords[0][0] for i in range(4): m = max(m, self.coords[i][0]) return m def minY(self): m = self.coords[0][1] for i in range(4): m = min(m, self.coords[i][1]) return m def maxY(self): m = self.coords[0][1] for i in range(4): m = max(m, self.coords[i][1]) return m def rotatedLeft(self): if self.pieceShape == Tetrominoes.SquareShape: return self result = Shape() result.pieceShape = self.pieceShape for i in range(4): result.setX(i, self.y(i)) result.setY(i, -self.x(i)) return result def rotatedRight(self): if self.pieceShape == Tetrominoes.SquareShape: return self result = Shape() result.pieceShape = self.pieceShape for i in range(4): result.setX(i, -self.y(i)) result.setY(i, self.x(i)) return result app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv) tetris = Tetris() tetris.show() sys.exit(app.exec_())
I have simplified the game a bit, so that it is easier to understand. The game starts immediately, after it is launched. We can pause the game by pressing the p key. The space key will drop the tetris piece immediately to the bottom. The game goes at constant speed, no acceleration is implemented. The score is the number of lines, that we have removed.
self.statusbar = self.statusBar() self.connect(self.tetrisboard, QtCore.SIGNAL("messageToStatusbar(QString)"), self.statusbar, QtCore.SLOT("showMessage(QString)"))
We create a statusbar, where we will display messages. We will display three possible messages. The number of lines alredy removed. The paused message and the game over message.
... self.curX = 0 self.curY = 0 self.numLinesRemoved = 0 self.board = [] ...
Before we start the game cycle, we initialize some important variables. The self.board variable is a list of numbers from 0 ... 7. It represents the position of various shapes and remains of the shapes on the board.
for j in range(Board.BoardWidth): shape = self.shapeAt(j, Board.BoardHeight - i - 1) if shape != Tetrominoes.NoShape: self.drawSquare(painter, rect.left() + j * self.squareWidth(), boardTop + i * self.squareHeight(), shape)
The painting of the game is divided into two steps. In the first step, we draw all the shapes, or remains of the shapes, that have been dropped to the bottom of the board. All the squares are rememberd in the self.board list variable. We access it using the shapeAt() method.
if self.curPiece.shape() != Tetrominoes.NoShape: for i in range(4): x = self.curX + self.curPiece.x(i) y = self.curY - self.curPiece.y(i) self.drawSquare(painter, rect.left() + x * self.squareWidth(), boardTop + (Board.BoardHeight - y - 1) * self.squareHeight(), self.curPiece.shape())
The next step is drawing of the actual piece, that is falling down.
elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Left: self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX - 1, self.curY) elif key == QtCore.Qt.Key_Right: self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX + 1, self.curY)
In the keyPressEvent we chek for pressed keys. If we press the right arrow key, we try to move the piece to the right. We say try, because the piece might not be able to move.
def tryMove(self, newPiece, newX, newY): for i in range(4): x = newX + newPiece.x(i) y = newY - newPiece.y(i) if x < 0 or x >= Board.BoardWidth or y < 0 or y >= Board.BoardHeight: return False if self.shapeAt(x, y) != Tetrominoes.NoShape: return False self.curPiece = newPiece self.curX = newX self.curY = newY self.update() return True
In the tryMove() method we try to move our shapes. If the shape is at the edge of the board or is adjacent to some other piece, we return false. Otherwise we place the current falling piece to a new position.
def timerEvent(self, event): if event.timerId() == self.timer.timerId(): if self.isWaitingAfterLine: self.isWaitingAfterLine = False self.newPiece() else: self.oneLineDown() else: QtGui.QFrame.timerEvent(self, event)
In the timer event, we either create a new piece, after the previous one was dropped to the bottom, or we move a falling piece one line down.
def removeFullLines(self): numFullLines = 0 rowsToRemove = [] for i in range(Board.BoardHeight): n = 0 for j in range(Board.BoardWidth): if not self.shapeAt(j, i) == Tetrominoes.NoShape: n = n + 1 if n == 10: rowsToRemove.append(i) rowsToRemove.reverse() for m in rowsToRemove: for k in range(m, Board.BoardHeight): for l in range(Board.BoardWidth): self.setShapeAt(l, k, self.shapeAt(l, k + 1)) ...
If the piece hits the bottom, we call the removeFullLines() method. First we find out all full lines. And we remove them. We do it by moving all lines above the current full line to be removed one line down. Notice, that we reverse the order of the lines to be removed. Otherwise, it would not work correctly. In our case we use a naive gravity. This means, that the pieces may be floating above empty gaps.
def newPiece(self): self.curPiece = self.nextPiece self.nextPiece.setRandomShape() self.curX = Board.BoardWidth / 2 + 1 self.curY = Board.BoardHeight - 1 + self.curPiece.minY() if not self.tryMove(self.curPiece, self.curX, self.curY): self.curPiece.setShape(Tetrominoes.NoShape) self.timer.stop() self.isStarted = False self.emit(QtCore.SIGNAL("messageToStatusbar(QString)"), "Game over")
The newPiece() method creates randomly a new tetris piece. If the piece cannot go into it's initial position, the game is over.
The Shape class saves information about the tetris piece.
self.coords = [[0,0] for i in range(4)]
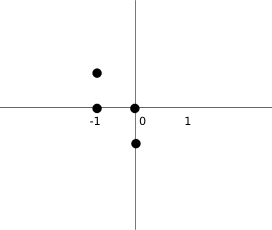
Upon creation we create an empty coordinates list. The list will save the coordinates of the tetris piece. For example, these tuples (0, -1), (0, 0), (1, 0), (1, 1) represent a rotated S-shape. The following diagram illustrates the shape.
When we draw the current falling piece, we draw it at self.curX, self.curY position. Then we look at the coordinates table and draw all the four squares.