Third-Party Automated Testing Tools
–Ь–∞—В–µ—А–Є–∞–ї –Є–Ј Wiki.crossplatform.ru

| 
|
| Qt Quarterly | –Т—Л–њ—Г—Б–Ї 16 | –Ф–Њ–Ї—Г–Љ–µ–љ—В–∞—Ж–Є—П | |
In the last Qt Quarterly issue, we presented QtTestLib, Trolltech'slightweight unit testing framework for Qt 4. We will now review KDExecuter and Squish, two powerful commercial tools that enable you tocreate sophisticated automated GUI tests – increasing the quality ofyour application and reducing testing costs in the long run.
–°–Њ–і–µ—А–ґ–∞–љ–Є–µ
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] KD Executor 2.1 by KDAB
KD Executor is a multi-purpose tool for recording scripts that can beplayed back at a later time, developed by Swedish-based Klar–іlvdalensDatakonsult AB (KDAB). It includes a user friendly test environmentthat can be used even by non-programmers – with the full power ofscripting behind it. Here are the main usage areas of KD Executor:
- Regression testing: Record test cases that should be executed on a regular basis. Besides just playing back your scripts, you can also ask KD Executor to check that certain properties of your interface are correct (any Qt property, such as a push button being disabled, as well as other "properties", such as a list box containing a certain item), compare screenshots, check assertions, etc.
- Demoing your software: Since KD Executor can be compiled into your executable, you can provide potential customers with a version of your application that only allows them to see your software run from a recorded script. Or you can record a demo for an unattended computer in a store front or at a trade show.
- Remote control: KD Executor can also be used to control your application remotely. Imagine customers asking for support by phone. Using KD Executor, you can ask them to start the application with a special flag and then control it yourself over the Internet.
Licensed versions of KD Executor include the complete source code, aprogrammer's manual, and comprehensive reference documentation. AKD Executor license entitles you to one year of technical support andupgrades. Maintenance contracts can then be extended at a favorablerate. KD Executor is available for all platforms supported by Qt. Theminimum Qt version required is 3.0.5.
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Smart Recording Technology
Unlike most competing products, KD Executor doesn't record raw X11 orWin32 events. This would not be satisfying in a real-life projectscenario where the playback situation might look a bit different fromthe recording situation (different font sizes, layouts, languages,etc.). Instead, KD Executor does the following:
- It records events for each widget individually rather than for the application as a whole. A pressed button located at position (100, 20) at record time will be pressed correctly during playback, even if it has been moved to position (400, 80).
- It records the intention rather than the actual action on many of Qt's widgets. For example, think of a QTabWidget, which consists of several tabs. During the recording session, you press the third tab. KD Executor will recognize a mouse event on the QTabBar and will record which tab was at that screen position.
This contributes to making KD Executor scripts very robust: Evenif the layout changes, the script will still work. In largeprojects, the recorded test cases are often a considerable investmentof time and money that should be protected as much as possible.
This smart recording technology is available for many of Qt'sbuilt-in widgets. If you develop custom widgets, you can use KDExecutor's extension mechanism to enable this smart recordingtechnology for your own widgets.
Moreover, KD Executor increases the efficiency of the communicationbetween testers (or customers) and developers. Instead of describinga defect in an application, testers can simply record the situationwhere the defect shows up and send the resulting platform-independentscript to the engineers. Scripts can be recorded as XML or asJavaScript (using QSA, Trolltech's official JavaScript/ECMAScriptimplementation).
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Main Operation Modes
The KD Executor Shell uses a simple and convenient approach totesting a Qt application. It lets you create and manage test suitesand test cases in a friendly graphical testing environment. One ofthe main design goals of the KD Executor Shell was to make it as easyto use as possible, even for non-programmers, while still keeping thefull power of scripting behind it.
More advanced users who already have a test environment in place mayuse KD Executor as a powerful record/playback engine, by runningand configuring it from the command line. This allows test cases tobe executed automatically from batch or scheduled jobs.
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Using the KD Executor Shell
Launching the KD Executor Shell gives you an overview of all testsuites, test cases, and test runs gathered in one table. A resulttable is located behind the result tab, with all performed testsordered and collected by date and time when the execution took place.
By recording user inputs, KD Executor quickly captures new tests.There are no complicated test scripts to write or debug. At any timeduring the capture process, you can probe your application to recordkey properties. The values of these properties become testbenchmarks. KD Executor's sophisticated test management subsystemallows you to replay these tests in any combination and automaticallyvalidate the execution of your application against thesetest benchmarks.
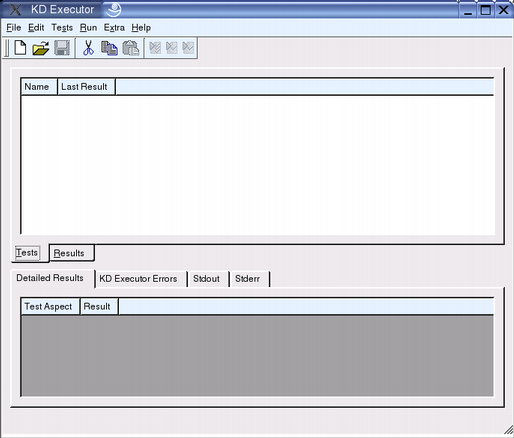
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] KD Executor Main Window
Detailed Results shows more informationabout a particular test result. It displays the different testaspects, and whether the test case failed or passed.
The tab labeled KD Executor Errors will display any internal errorsof the application under test that might occur during the executionof a test case. This is to prevent the test run from being locked up byany error dialogs.
|
Stdout and Stderr show the standard output and standarderror data coming from the application being tested, and are oftenuseful tools for finding out why a test case failed.
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Test Suite Table
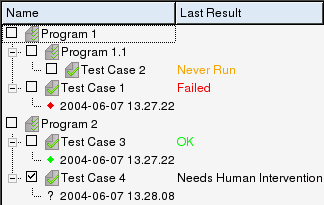
All information about test suites and tests is presented in a treeview. Test suites can contain both test cases and other test suites,whereas the test cases themselves contain all test runs executed onthem. The user can create, import, edit, or remove any of these itemsby right-clicking on the item and selecting the requested operationfrom the context menu.
|
The test suite tree can contain several test suites:
- The Last Result for a test case can have four different values: OK, Failed, Needs Human Intervention, or Never Run.
- Everywhere in the KD Executor Shell, context menus provide fast access to the most common operations.
- Right-clicking on any of the items will display a menu with options for that specific item.
The hierarchical layout of test suites and test cases enablesyou to organize the test cases according to any structure thatmatches your application or quality assurance (QA) organization. Allinformation about a test suite or a test case can be viewed at aglance in a separate dialog.
If you have recorded any Qt properties, you can view their baselinevalues or the values that were recorded during a test execution bylaunching the Property Editor which lists all properties pickedduring script recording. If the Property Editor was invoked on a testresult, it will also show the actual value of the property duringplayback. A similar Assertion Editor lets the user view theassertions for a particular test case, as well as the results duringtest runs.
Logs and tests generated on one platform can be run on any otherplatform supported by Qt. KD Executor also provides test run reportsin HTML format. Publishing those reports on an intranet site is aconvenient way of communicating the test results within an organization.
| While recording a test case, a number of actions are available from asidebar that is launched together with the application under test. Thisallows the user to invoke the property picker, to take a snapshot, etc. Itis possible to bind these functions to keys. |
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Using the Raw KD Executor Engine
There are two main ways to use the KD Executor core engine.
- Pre-loading: Simply type kdexecutor on the command line before the name of your application. The KD Executor configuration dialog will pop up, allowing you to set various options. Most settings can also be specified on the command line.
- Source code modification: It is possible to compile KD Executor into your binary. This is useful if you want to limit the usage of your software (e.g., for playback-only demo versions), or if you want to use KD Executor in an already tailored C++ test environment.
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Squish 2.1 by froglogic
Squish 2.1 is latest version of the automated testing tool fromfroglogic, a German software vendor that was founded bytwo former Trolltech senior software engineers. Squish providesa fully-featured automated GUI test tool for Qt applicationsthat competes with established tools such as WinRunner, RationalRobot, and SilkTest while adding the extra value of a tight andcomplete Qt integration.
Squish allows you to record tests using several popular scriptinglanguages. You can add verification points to the scripts to ensurethat the application is behaving correctly, and rerun the tests asunattended regression tests.
Squish can be used to test Qt 3.x and Qt 4.x applications on Windows,Linux, Mac OS X, and several commercial Unix variants. Squish canalso be used to test Qt/Embedded 2.3, including Qtopiaapplications, running on the target device or inside Qt's VirtualFramebuffer The product is packaged with its complete source code,thus enabling a compile-time adaption to any particular Qtconfiguration.
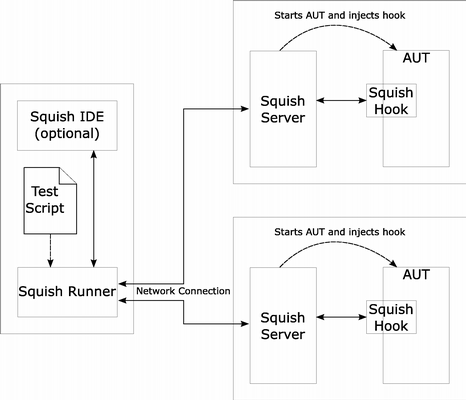
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] The Architecture
For testing with Squish, no modification of the application under test(AUT) is required. On application startup, Squish dynamically injects amodule into the application's process space. The module takes overcontrol and provides a TCP/IP network connection between the AUT andthe tool driving the test.
This architecture allows for applications to be tested ondifferent remote hosts, as well as multiple AUTs in parallel,which can be useful for testing complex client--server systems.
|
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Scripting Languages and Bindings
Squish currently supports Python, JavaScript, and Tcl, and it isexpected that a future version will support Perl as well. Usinga standard scripting language over a "vendor script" offersthe following benefits:
- Familiarity with the language.
- Wide range of resources (documentation, tutorials, books).
- Rich set of language features (e.g., control flow structures).
- Availability of third-party extension modules.
Squish extends the native script language with test-related functionsand complete bindings to Qt, enabling the creation of very powerfultest scripts. It is even possible to automatically create scriptbindings for any C++ library or application code, which can then beaccessed from all available scripting languages.
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Recording a Test
Squish organizes tests in test suites. A test suite consists of anumber of test cases and possibly shared data and scripts.
A test case contains a test script which can be implemented in any ofthe supported scripting languages. Additionally, we canattach test data to a test case.
To create a test script, we normally start by "recording" it,meaning that the test engineer performs the actions on the AUT whichshould be tested while Squish is running. The result is a script thatcan be replayed at will. Thanks to this recording facility, entiretests can be created without writing a single line of code. Apartfrom being convenient, this allows the involvement of test engineerswho don't have coding skills.
The following JavaScript test script was recorded by Squish for Qt 4'sSpreadsheet demo. The user changed the value of the expenses for"Hotel" from 300 to 400 and exited the application:
function main() { doubleClickItem(":Spreadsheet.Table1.QWidget1", "300", 95, 17, 0, Qt.LeftButton); type(":Spreadsheet.Table1.QLineEdit1", "<Backspace>"); type(":Spreadsheet.Table1.QLineEdit1", "<Backspace>"); type(":Spreadsheet.Table1.QLineEdit1", "<Backspace>"); type(":Spreadsheet.Table1.QLineEdit1", "400"); type(":Spreadsheet.Table1.QLineEdit1", "<Return>"); activateItem(":Spreadsheet.QMenuBar1", "File"); activateItem(":Spreadsheet.QMenuBar1.QMenu3", "Exit"); }
As this script illustrates, Squish records high-level actions ratherthan low-level events. For example, it records a double-click on aspecific widget rather than mouse events for specific screencoordinates. Similarly, it records menu item activations instead ofindividual mouse events. This makes the script more readable andmaintainable, but also more robust against changes in theapplication's user interface. This robustness is crucial if the testscript is expected to run correctly on different platforms andcomputers.
The above script could now be run to see if the applicationbehaves correctly – however, the goal of automated testing is to performthis kind of verification without any human interaction. This isaccomplished using verification points. A verification point comparesan actual result against an expected value. Comparisons are normallybased on properties of objects (e.g., the text of a spreadsheet cell).
If at some point it is necessary to change a small part of a testscript, Squish lets us run a test until a certain point and recordfrom there, inserting the newly recorded code into the existingscript instead of recording the entire script.
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Object Property Verifications
To continue with our example, we now want to check that the value for totalexpenses is recalculated correctly after the value for hotel expenseswas changed. Inserting a verification point can be done in Squishusing a comfortable point and click interface.
Verification points are stored in XML files and can be edited usingan integrated editor. The script commandtest.vp( "\"VP_ChangeHotelExpense\"") is insertedautomatically into the test script and will perform the comparison.(VP_ChangeHotelExpense is a unique identifier of the verificationpoint.) Property verifications can also be expanded into scriptstatements. For example, the verification point from our examplechecking the hotel expenses and total sum in the table would resultin the following script calls:
test.compare(findObject(":Spreadsheet.Table1.item_7/1") .text, "400"); test.compare(findObject(":Spreadsheet.Table1.item_9/4") .text, "22433");
It is also possible to add such verifications to the script manuallyto perform more sophisticated checks. These checks can use any controlflow statement and any part of the Qt API. Here's a Python examplethat checks that a QListView contains exactlythree items with the text "Banana":
listview = findObject("MainWindow.listView") found = 0 item = listView.firstChild() while not isNull(item): if item.text(0).contains("Banana"): found += 1 item = item.nextSibling() test.compare(found, 3, "Check number of Bananas")
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Screenshot Verifications
There are some cases where the only way to check for correctness is tocompare a widget to a previously taken screenshot (the expectedresult). This is usually the case for graphing widgets, drawingcanvases, etc. Squish supports the creation of screenshot comparisonsby choosing the widgets to verify.
To make screenshot comparisons more robust, test engineers can definewhich regions of the image are relevant to the comparison. This canbe used to filter out labels in a diagram, which might change theirappearance depending on the machine and font settings.
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Running a Test
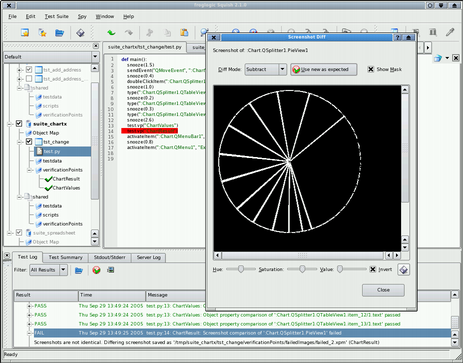
After having created a test, it can simply be executed in the SquishIDE. The results of the verification points and any other errors whichmight have occurred are listed in the result log. Clicking on a testresult takes the user to the file and line of the corresponding testscript.
|
The IDE also allows for a closer inspection of test failures bydisplaying the deviation between expected and actual results. In thecase of screenshot comparisons, multiple ways are offered tovisualize the differences. In the screenshot above, all changes to achart diagram are displayed in white (the Chart example, locatedin Qt 4's "examples/itemviews/chart" directory, served as theAUT).
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Automating Test Runs and Regression Testing
The ultimate goal of automated GUI testing is to run the tests inunattended mode. Squish includes a set of command-line tools thatmake it easy to integrate the tests into a cron job, a Windowsservice, or a test management tool. This needs to be done onlyon one machine on the network; the command-line tool executing thetests can run the tests on other machines, regardless of theoperating systems in use.
Test results can be generated as XML files, which can bepost-processed to create HTML output, or fed into a test management orbug tracking system.
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Robustifying Tests
To create robust and maintainable tests, test engineers will oftenedit the recorded tests to factor out common code. For example, theGUI actions required to open a file in the AUT might be put in aseparate script function. Such functions are available to all thetest scripts from a test suite.
If scripts are manually written, the script coders need to know thenames of the objects and properties of the AUT. This can be achievedeasily using Squish's Spy, a tool that inspects the object hierarchyand properties of a running Qt application.
Another Squish feature that eases the task of creating robust testsis the object map. It maps symbolic names of objects to the realnames in the application. In scripts, symbolic names are used. So whensome object names in the application change, only the real names inthe object map need to be updated; no script code needs to bechanged.
A common method used to make a test easily extensible is to introducedata-driven testing. With this appoach, the data is written into aseparate file or a database, instead of being hard-coded in thescript. The test is then executed for each data record. This way,tests can be extended without touching the test script at all. Squishprovides APIs and tools to take advantage of data-driven testing.
[–њ—А–∞–≤–Є—В—М] Conclusion
We have seen how KD Executor and Squish can be used to createsophisticated automated GUI tests which will increase the quality ofapplications and reduce testing costs in the long term. If you areserious about quality assurance, we recommend that you try bothproducts and choose the one that best suits your needs.
More information about KD Executor, including free evaluationversions, is available fromwww.kdab.net/kdexecutor.
To learn more about Squish and request an evaluation version, visit www.froglogic.com or contact squish@froglogic.com.
